Atletik Performansı Arttıran En İyi 4 Besin Desteği:
İster amatör bir koşucu veya futbolcu olun ister sadece haftasonları eğlence amaçlı spor yapan biri olun, atletik performansınızı geliştirmek için düzenli tüketmenizi önerdiğimiz besin takviyeleri ile daha hızlı koşabilir, halı sahada veya çim sahada daha dayanıklı bir oyuncu olabilirsiniz. Önerdiğimiz besin takviyeleri, her seviyede antrenman yapan kişiler tarafından rahatlıkla , önerilen dozajlarında tüketilebilir.

| Kreatin Monohidrat | Kafein |
| Önerilen Doz: Günde 3-5 Gram arasında | Önerilen Doz: Vücut ağırlığınızın her bir kilosu için 1.8-2.7 Mg. alabilirsiniz. |
| Kreatin desteği, oyunlarda gösterdiğiniz performansınızı arttırmaya destek olur. | 60 Dakikalık bir müsabakada veya antrenman öncesinde 150-300 Miligram arasında alabilirsiniz. |
| Nutrend Creatine Monohydrate 500 Gram - Besin Destek | Nanox Coffee Coach Kahve 20 Poset - Besin Destek |

| Beta-Alanin | Protein |
| Araştırmalar Beta-Alanin molekülleri içeren besin takviyelerinin antrenman yorgunluğunu azalttığını ve Kreatinin faydalarını arttırdığını işaret etmektedir. Bunun yanında yağsız kitle kazancına yardım eder, anti-oksidan özelliği ile yaşlanmayı geciktirici etkiler gösterir. | Antrenman seviyeniz arttıkça, kas yıkımını önlemek daha öncelikli hale gelir ve Proteinler kas kazanımının temel besin maddeleridirler. |
| Önerilen Doz: Günde 3-6 Gram arasında | Önerilen Doz: Günde 20-25 Gram arasında Whey Protein |
| San Nutrition Bcaa PRO 5000 - 345 Gr + Beta Alanine - Besin Destek | Hardline Whey 3 Matrix 2300 Gr - Besin Destek |
Referanslar
Buford, T. W., Kreider, R. B., Stout, J. R., Greenwood, M., Campbell, B., Spano, M., ... & Antonio, J. (2007). Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 4(6), 6.
Van Loon, L. (2003). Effects of creatine loading and prolonged creatine supplementation on body composition, fuel selection, sprint and endurance performance in humans. Clinical Science, 104, 153-162.
Cooper, R., Naclerio, F., Allgrove, J., & Jimenez, A. (2012). Creatine supplementation with specific view to exercise/sports performance: an update. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 9(1), 33.
Cox, G., Mujika, I., Tumilty, D., & Burke, L. (2002). Acute creatine supplementation and performance during a field test simulating match play in elite female soccer players. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 12(1), 33-46.
Jones, A. M., Atter, T., & Georg, K. P. (1999). Oral creatine supplementation improves multiple sprint performance in elite ice-hockey players. The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 39(3), 189-196.
Chilibeck, P. D., Magnus, C., & Anderson, M. (2007). Effect of in-season creatine supplementation on body composition and performance in rugby union football players. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 32(6), 1052-1057.
Glaister, M., Howatson, G., Abraham, C. S., Lockey, R. A., Goodwin, J. E., Foley, P., & McInnes, G. (2008). Caffeine supplementation and multiple sprint running performance. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 40(10), 1835-1840.
Greer, F., McLean, C., & Graham, T. E. (1998). Caffeine, performance, and metabolism during repeated Wingate exercise tests. Journal of Applied Physiology, 85(4), 1502-1508.
Stuart, G. R., Hopkins, W. G., Cook, C., & Cairns, S. P. (2005). Multiple effects of caffeine on simulated high-intensity team-sport performance. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 37(11), 1998-2005
Foskett, A., Ali, A., & Gant, N. (2009). Caffeine enhances cognitive function and skill performance during simulated soccer activity. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 19(4), 410-423.
Hoffman, J. R., Ratamess, N. A., Faigenbaum, A. D., Ross, R., Kang, J., Stout, J. R., & Wise, J. A. (2008a). Short-duration beta-alanine supplementation increases training volume and reduces subjective feelings of fatigue in college football players. Nutrition Research, 28(1), 31-35.
Tartibian, B., Maleki, B. H., & Abbasi, A. (2009). The effects of ingestion of omega-3 fatty acids on perceived pain and external symptoms of delayed onset muscle soreness in untrained men. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine, 19(2), 115-119.
Smith, G. I., Atherton, P., Reeds, D. N., Mohammed, B. S., Rankin, D., Rennie, M. J., & Mittendorfer, B. (2011). Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids augment the muscle protein anabolic response to hyperinsulinaemia-hyperaminoacidaemia in healthy young and middle-aged men and women. Clinical Science, 121(6), 267-278.
http://www.besindestek.com | Yaşamını Destekle, Limitlerini Zorla!














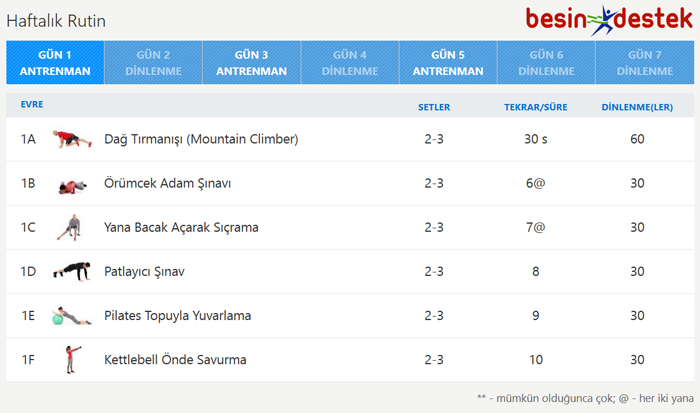



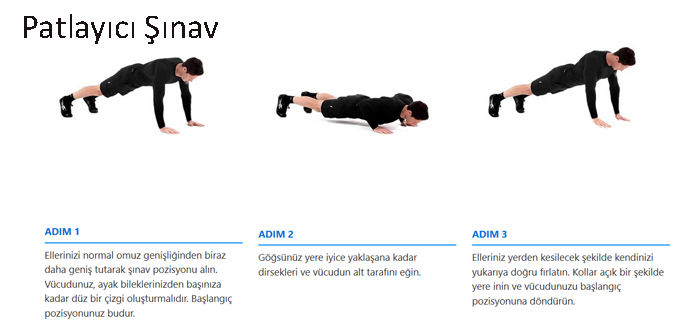

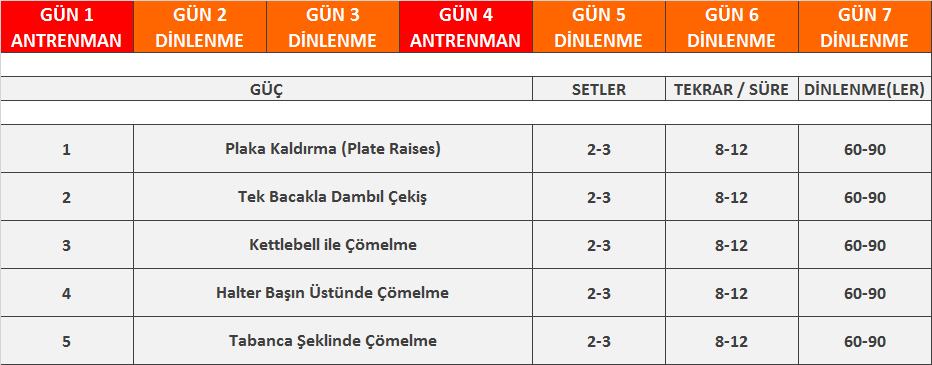
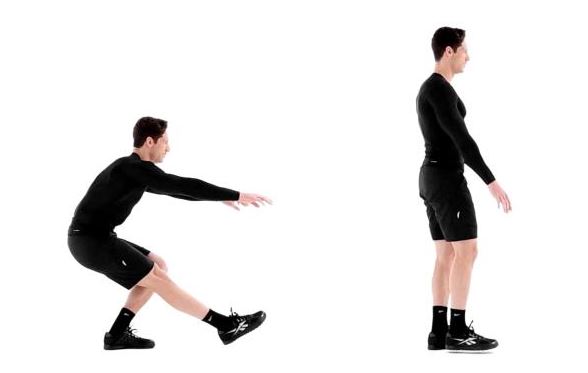
 ADIM 1
ADIM 1